(1) insulin resistance and (2) β-cell dysfunction: inadequate insulin secretion in the face of insulin resistance and hyperglycemia Sedentar...


(1) insulin resistance and (2) β-cell dysfunction: inadequate insulin secretion in the face of insulin resistance and hyperglycemia Sedentar...

chronic autoimmune attack on β cells manifestations of the disease (hyperglycemia and ketosis) occur late in its course, after more than 90%...

Type 1 diabetes (β-cell destruction): Immune-mediated, Idiopathic Type 2 diabetes (insulin resistance with relative insulin deficiency) Matu...

Infectious: viral damage to mucosal epithelium Rotavirus Caliciviruses Enteric adenoviruses Astroviruses Infectious: enterotoxin mediated Vi...
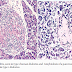

Malabsorption Defective intraluminal digestion Primary mucosal cell abnormalities Reduced small intestinal surface area Lymphatic obstructio...

Disaccharidase (lactase) deficiencies Lactulose therapy (for hepatic encephalopathy, constipation) Prescribed gut lavage for diagnostic proc...

Hernia - Inguinal Hernia - Opened. Intestinal Obstruction: Intussusception: Volvulus: Diverticula:


limited to the mucosa and submucosa begins in the rectum and extends proximally in a continuous fashion migratory polyarthritis, sacroiliiti...

Used to be called " terminal ileitis " or " regional enteritis ” extra-intestinal complications of immune origin, such as uve...

result from an abnormal local immune response against the normal flora of the gut, and probably against some self antigens, in genetically s...

previous exposure to ionizing radiation they may be well circumscribed and even encapsulated; in other instances, they infiltrate the adjace...

nodular goiter may predispose RAS mutations in follicular adenomas and carcinomas suggests that they may be related tumors Hürthle cell vari...

Like normal C cells, medullary carcinomas secrete calcitonin, the measurement of which plays an important role Neuroendocrine cells may secr...

multinodular goiter, or other differentiated carcinoma are usually present bulky masses that typically grow rapidly beyond the thyroid capsu...

Papillary carcinoma: (75% to 85%): novel fusion genes, known as ret/ PTC , which constitutively activate RET and the downstream MAP kina...

Although the vast majority of adenomas are nonfunctional, a small proportion produces thyroid hormones (" toxic adenomas ") Activa...

Solitary nodules, in general, are more likely to be neoplastic than are multiple nodules. Nodules in younger patients are more likely to be ...

Giant cell /temporal arteritis - the most common of the vasculitides. It is a granulomatous inflammation of arteries of large to small size...

An inflammatory disorder of the aortic arch and its major branches, with localized stenosis or occlusion An auto-immune basis has been propo...

Systemic vasculitis affecting medium and small muscular arteries- kidneys 85%, heart 75%, liver 65%, GI 50% Morphology - acute (fibrinoid n...

Systemic vasculitis of small arteries and veins. Granulomatous inflammation of nose, sinuses, lung, kidney Anti Cytoplasmic Neutrophil Antib...

Deficiencies of Clotting factors Onset - delayed after trauma Deep bleeding Into joints - Hemarthroses Into deep tissues – Hematoma large sk...

Obstetric Complications Abruptio placentae Retained dead fetus Septic abortion Amniotic fluid embolism Toxemia Infections Gram-negative seps...

Decreased platelet count. Is characterized by spontaneous bleeding which is evident at platelet count below 20,000/μL , 20,000 to 50,000 may...

Autoimmune in origin. may occur in isolation or in association with an underlying condition such as lymphoma or collagen vascular disease ...

Heparin – binds to AT III – inactivation of factors IIa, IXa, Xa, XIa, XIIa. – used as anticoagulant. Large molecular weight substance. On ...

Relative: Reduced plasma volume (hemoconcentration) Primary: Abnormal proliferation of myeloid stem cells, normal or low erythropoietin leve...

Aplastic anemia is a disorder characterized by the suppression of multipotent myeloid stem cells, with resultant anemia, thrombocytopenia, a...

caused by antibodies that react against normal or altered RBC membranes. Immunohemolytic anemias are classified on the basis of the nature o...

MHA is the form of intravascular hemolysis These disorders is characterized by the presence of vascular lesions that predispose the circula...

G6PD – is a rate limiting enzyme in HMP shunt pathway . This pathway is responsible for production of NADPH which is required in number of ...
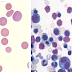
Autosomal dominant / Autosomal recessive (25% more severe) pattern of inheritance Spherodial RBCs – which makes RBC less deformable and more...

Microvasuclar Ischemia. Autosplenectomy - Intially there is moderate splenomegaly caused by congestion of the red pulp with masses of RBCs ...

Sickle cell Anemia is hemoglobinopathie , where substitution of valine for glutamic acid at the sixth position of the β-chain produces HbS. ...

Anemia that are associated with decreased RBC life span. Hemolytic anemias are characterized by an increased rate of RBC destruction, a comp...

Thalassemia syndromes are a heterogenous group of inherited disorders caused by genetic lesions leading to decreased synthesis of either alp...

I. Infections Nonspecific splenitis of various blood-borne infections (particularly infective endocarditis) Infectious mononucleosis Tubercu...

Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin) Deficiency Anemia: can also cause a demyelinating disorder involving the peripheral nerves and, ultimately and most ...

Folic Acid Deficiency Decreased intake Inadequate diet—alcoholism, infancy Impaired absorption Malabsorption states Intrinsic intestinal dis...